After arthritis and heart disease, hearing loss is the most common physical condition in adults. According to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, approximately 37.5 million adults in the U.S. suffer from hearing loss. That equates to about one in six U.S. adults.
With the condition being so prevalent, it is important to know the causes, preventive measures and possible treatments for hearing loss.
Types of Hearing Loss
Sensorineural
When inner ears nerves become damaged and can no longer transmit signals to the brain it is referred to as sensorineural hearing loss. Noises, particularly speech, will often sound like mumbling to patients suffering from this condition. Most often, sensorineural hearing loss is permanent and is not medically or surgically treatable. However, patients can be helped with the use of hearing instruments.
Conductive
Conductive hearing loss is caused by disorders in the outer or middle ear that prevent sound from carrying to the inner ear. It can be caused by such things as an ear infection, tumor, trauma or fluid or an object in the ear (such as wax buildup). This condition causes noise to sound faint, distorted or both. Conductive hearing loss can be treated as long as it is done so early on.
Mixed
As the name implies, mixed hearing loss comprises both sensorineural and conductive components. It is an indicator that there are issues with both the inner ear as well as the outer and/or middle ear.
Causes
There is a long list of causes that can contribute to hearing loss. Some of the most common are:
Presbycusis
Presbycusis simply refers to the gradual loss of hearing that occurs as we age. According to Your Hearing Network, age-related hearing loss occurs in one out of three people over the age of 60 and two-thirds of the population over the age of 70. Presbycusis is the most common type of Sensorineural Hearing Loss and is most commonly the result of changes in the inner ear of a person as they age.
Noise
Sudden or prolonged exposure to loud noises can damage the hair cells in your ears and lead to temporary or permanent hearing loss.
Trauma
Trauma to your ears can damage your eardrum. This includes everything from having an object get inserted into your ear, a viral infection and even experiencing pressure difference such as from plane travel or scuba diving.
Wax
Ear wax serves an important purpose to lubricate, protect and keep ears clean. However, if your body produces too much wax it can block sound from reaching your inner ear.
Oxotoxicity
Oxotoxicity refers to anything that may be toxic or damaging to the ear. This is mainly a concern as a side effect of other medications you may be taking. For example, the chemotherapy needed to treat cancer may cause hearing loss.
Diabetes
Diabetes cause circulatory issues and other conditions that can contribute to hearing loss. In fact, the National Institute of Health found that hearing loss is about twice as common in adults with diabetes compared to those who do not have the disease.
Otosclerosis
Otosclerosis is a hereditary disorder characterized by bone overgrowth in the inner ear that causes progressive hearing loss.

Lifestyle Impact
Hearing loss can have a dramatic effect on your everyday life.
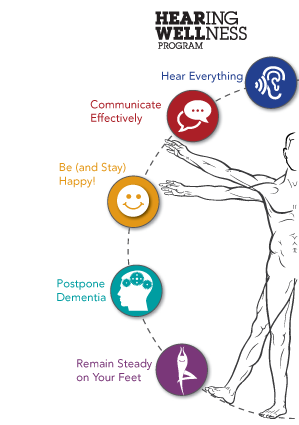
Proper hearing ability allows you to both understand and communicate with people and the world around you, which can significantly improve your quality of life. In fact, Your Hearing Network found that 36% of patients who begin wearing hearing aids experienced improved overall mental health.
But we use our ears for more than just hearing sounds. Among other roles, they play a big role in controlling our balance. Patients with hearing loss suffer falling incidents at a rate three times higher those with good hearing.
Believe it or not, good earing can also help postpone dementia. Ears don’t just hear sounds, they identify frequency, pitch, location and many other details instantly. Absorbing all this information helps keep your mind sharp. Your Hearing Network states that people with moderate or severe hearing loss have a 55% increase in risk of dementia.
Preventing Hearing Loss
The best way to treat hearing loss is to try to prevent it from happening in the first place. Therefore, you should get your hearing checked regularly. For adults over the age of 55, this means on an annual basis. Not only is early diagnosed hearing loss usually easier to treat, but it can also be an indicator for other health problems.
Loud noises and high decimals can wreak havoc on your ears. Prolonged exposure to these sounds can severely damage your hearing. If you find yourself in an environment where these noises are unavoidable, make sure to wear earplugs.
This may sound counterintuitive but avoid Q-tips and cotton swabs when removing excess ear wax. These products push wax deeper into the ear canal, blocking sound from getting to the inner ear. Instead, use ear wax removal kits that loosen the wax to be washed out. Or have a doctor remove the wax.
Possible Treatments
If you do suffer from hearing loss, there are numerous hearing aid options that can help restore your hearing. An audiologist can help you choose the one that best suits your condition and lifestyle. Find a hearing healthcare professional near you.